Introduction
Blinatumomab is a bispecific T-cell engager antibody designed to redirect CD3+ T cells to bind to CD19+ target cells in relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). Measurable residual disease (MRD) is a significant prognostic factor for relapse and overall survival in B-ALL. Blinatumomab consolidation therapy has been shown to improve MRD remission (<10 -4), as detected by multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) or reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and survival outcomes in children with high-risk first relapsed B-ALL. The next-generation sequencing (NGS)-MRD is a highly sensitive technique that can detect very low levels of MRD (<10 -6) in patients who were considered “MRD negative” by less sensitive MFC or PCR technologies. Early achievement of NGS-MRD negativity (<10 -6) can help in identifying patients who have a very low risk of relapse. It has been suggested that blinatumomab treatment could help to attain deeper responses than that measured with a MRD sensitivity level of 10 -4. However, data on blinatumomab clearing MRD with high sensitivity of 10 -6 remain scarce. Hence, we evaluated the effectiveness of blinatumomab in eradicating extremely low level of MRD (<10 -6), as detected by NGS, in children with B-ALL.
Methods
Pediatric B-ALL patients who were MFC-MRD negative (<10 -4) but NGS-MRD positive (sensitivity of 10 -6) after chemotherapy followed by blinatumomab consolidation therapy between October 2021 and February 2023, were studied retrospectively. At diagnosis, NGS analysis was performed by high-throughput deep level sequencing using the Seq-MRD ® (ImmuQuad Biotech, Hangzhou, China) to detect clonal rearrangements. Genomic DNA was extracted from bone marrow samples using QIAamp DNA Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), amplified by quantitative PCR and sequenced using the Illumina® Novaseq PE150 (Illumina ® Novaseq, San Diego, USA) platform. The sequences of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) (IGH -VDJ), IGH-DJ, immunoglobulin kappa light chain (IGK), immunoglobulin kappa deleting element (IGKDE) and immunoglobulin light chain (IGL) were assessed for clonality with dominant index sequence(s).
Results
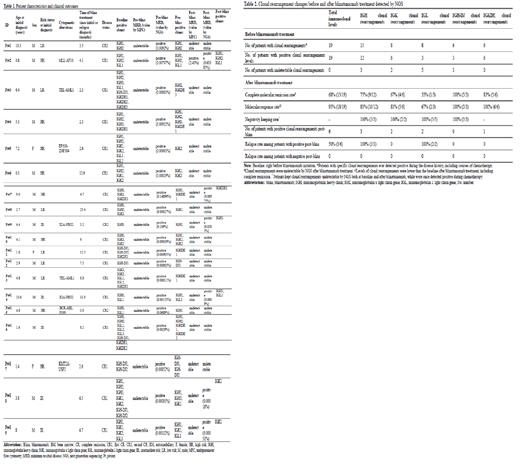
Overall, 19 patients were enrolled. The baseline patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Median age at diagnosis was 4.4 years (range 0.3-10.6), with males accounting for 84% of patients. Eight patients (42%) had at least 1 unfavorable genetic abnormality (i.e., KMT2A rearrangement, E2A-PBX1). Seventeen (89%) patients had ≥2 Ig clonal rearrangement at diagnosis. In total, NGS detected 71 clonal rearrangements, including 27 IGH clonal rearrangements in 15 (79%) patients, 9 IGH-DJ in 6 (32%), 14 IGK in 8 (42%), 6 IGKDE in 9 (32%), and 12 IGL in 8 (42%) patients.
All patients achieved hematological complete response (CR) with MFC-MRD <10 -4 after the induction or consolidation chemotherapy. However, all these patients were identified to be MRD positive by NGS, including NGS-MRD >10 -6 and positive but not quantifiable (NGS-MRD <10 -6). Though the patients were MFC-MRD negative, 19 IGH clones, 4 IGH-DJ clones, 8 IGK clones, 7 IGKDE clones and 3 IGL clones were still persisted. After blinatumomab, MRD negativity rate by MFC was 95% (18/19) and the NGS-MRD negativity rate was 68% at 10 -6 (13/19). The rate of MRD clearance after blinatumomab per NGS was 69% and 67% in CR1 and CR2 patients, respectively. The clearance rates of IGH, IGK, IGL, IGH-DJ, and IGKDE were 75%, 67%, 33%, 100%, and 83%, respectively (Table 2). Three NGS-MRD negative patients with available NGS-MRD at pre-, mid-, and post-treatment achieved MRD clearance rapidly after blinatumomab treatment that was maintained durably through day 28. Three of 6 NGS-MRD positive patients relapsed after blinatumomab with 3 being IGH positive and 2 being IGL positive.
Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, for the first time it has been demonstrated that blinatumomab could further eradicate MRD in patients achieving MFC-MRD <10 -4. Advanced MRD detection using NGS and blinatumomab made deeper molecular remission in B-ALL patients achievable. Further large-scale studies are warranted to verify the prognostic value of NGS in detecting lower levels of MRD in ALL patients treated in the current immunotherapy era.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal